JPMorgan Chase kicked off bank earnings season by raising lots of questions about its growth prospects — and everybody else's.
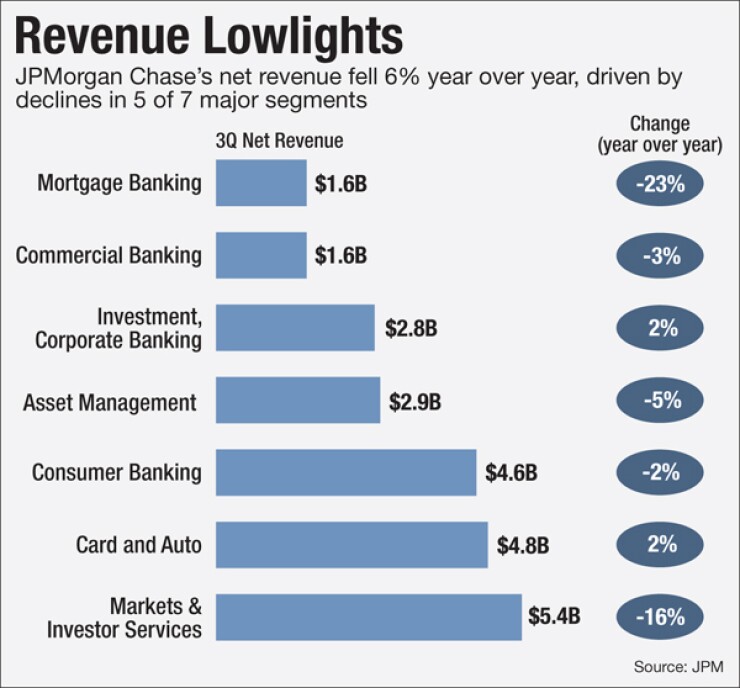
Though mortgage banking net income rose 29% in the third quarter, to $602 million, the unit took a hit as net revenue fell 23% to $1.6 billion due to lower servicing revenue.
Origination margins were also down, primarily because of the shift in the mix from refinance activity to home purchases, and from retail loan originations to correspondent lending.
The bank expects noninterest revenue for mortgages to be down $250 million year over year, Marianne Lake, JPMorgan's chief financial officer, told analysts, bringing total net interest revenue down by roughly $1 billion.
Total net revenue fell 6.4% in the third quarter compared with a year earlier, and it wasn't just because mortgage banking fees plummeted and trading was choppy. Net interest income contracted and slowdowns occurred in consumer operations, commercial banking and asset management.
Even strong third-quarter loan growth of 9% was mitigated by still-tight margins. A warning about JPMorgan's fourth-quarter earnings estimates, and new concerns about the economy, only heightened concerns about the industry's strength with more big banks scheduled to report this week.
"Analysts' [fourth-quarter] estimates appear high," cautioned Lake, citing ongoing volatility in trading revenue.
Certainly the Fed's decision to take a pass on raising interest rates so far this year has made it difficult for big banks to generate much momentum, and now there is chatter about the possibility of a recession.
In one exchange during JPMorgan's earnings conference call, Mike Mayo, an analyst at CLSA, tried to draw JPMorgan Chairman and CEO Jamie Dimon into a discussion about the U.S. economy, but Dimon let Lake take the lead.
"We would say the U.S. economy is doing pretty well," Lake said reassuringly. "We're seeing good demand for loans in the consumer space and reasonably good sentiment in the business-banking space, and our core loan growth numbers do show that. There's nothing particularly bumpy in the loan-growth numbers."
Lake also said she had a "different perspective" on the disappointing monthly jobs report released by the Labor Department this month that fueled economic concerns.
"While [the jobs report] was somewhat lower than people were expecting or possibly hoping for, it's still at around 140,000 [jobs created in September], almost two times what would be required to have stable unemployment," she said. "You can't overreact to it. It's not that we're seeing anything that's causing us any concern in our outlook for the fourth quarter; it [was] pretty solid, I think."
To be sure, JPMorgan was able to produce robust profits. The bank reported a 22% jump in third-quarter earnings to $6.8 billion, or $1.68 a share, compared with $5.57 billion, or $1.35 a share, in the same period a year earlier. JPMorgan earned $1.32 a share excluding $2.2 billion of tax benefits and other one-time items. A consensus of analysts surveyed by Bloomberg had expected earnings of $1.38 a share.
Some of the profit improvement has come from cost reductions; JPMorgan said it had cut 10,000 employees through Sept. 30.
Total loans were $809.5 billion, 9% higher than a year earlier. But the yield on interest-earning assets dipped to 2.16% in the third quarter, compared with 2.19% a year earlier. The bank expects core loan growth of 15% in the fourth quarter.
JPMorgan took the biggest hit in the quarter to its markets and investor services business line, where revenue fell 16% to $5.4 billion. But Lake emphasized that despite the drop in trading volume, the bank was still able to capitalize on market volatility.
"Look, the situation for us in markets was one where there was volatility regardless of how you want to characterize it and people were acting — our clients were acting on the back of that. We were able to capitalize on that flow," she said. "[It was] more about low levels of activity, people on the sidelines. It was tougher to make money because less was happening rather than anything else more significant than that. So far in the fourth quarter we're two weeks in, it's too early to say, but there's not been a tremendous change in the landscape."




